
TONIGHT: Lyme Disease Recipes for healing at TOHP Burnham Public Library Essex

My View of Life on the Dock

 Perhaps you didn’t think much of all the little baby squirrels running about your neighborhood this past summer. We had half a dozen nests on out street, and each nest appeared to have half a dozen babies. Early in the morning I would often see the young families playing in, around, and under our neighbors cars, scampering up and down trees, and leaping about the branches. I wasn’t paying too much attention, until we began to notice large toothy chunks missing from my unripe peaches. Half eaten peaches, still on the branch, along with disappearing fruit, plagued our little tree until by harvest time we had little more than a handful, when usually we have baskets full.
Perhaps you didn’t think much of all the little baby squirrels running about your neighborhood this past summer. We had half a dozen nests on out street, and each nest appeared to have half a dozen babies. Early in the morning I would often see the young families playing in, around, and under our neighbors cars, scampering up and down trees, and leaping about the branches. I wasn’t paying too much attention, until we began to notice large toothy chunks missing from my unripe peaches. Half eaten peaches, still on the branch, along with disappearing fruit, plagued our little tree until by harvest time we had little more than a handful, when usually we have baskets full.
 We found the culprit(s) mid-summer, brazenly scurrying and chomping through the peach tree. The squirrels ate all our blueberries, too, and most recently, have been depositing the large green balls of the Black Walnut tree fruits on our front porch.
We found the culprit(s) mid-summer, brazenly scurrying and chomping through the peach tree. The squirrels ate all our blueberries, too, and most recently, have been depositing the large green balls of the Black Walnut tree fruits on our front porch.
Why the squirrelnado? During the 2017 growing season there was a bumper crop of acorns, which means many more adults went into winter with a full belly and an ample supply of acorns in their pantries. A greater number than usual survived the winter, which translates to many more baby squirrels in the spring of 2018. This year’s acorn crop has been smaller than average. The squirrels are desperately trying to stockpile food. Not only are they eating foods they don’t normally eat, but they are also exhibiting extremely at risk behavior. Driving along New England highways and byways, you may have observed a great many dead squirrels as both roadkill and laying alongside the road.
If a squirrel runs out in front of your car when traveling at high speed on the highway, it is best not to swerve. I know that sounds counterintuitive, but the squirrels look at the car as a large oncoming predator. By swerving, you confuse the critter, and run the risk of injuring yourself and/or another party.
With far fewer acorns, not as many squirrels will survive the winter. Will we see an upswing in Lyme disease next summer? I imagine so. White-footed Deer Mice and Eastern Chipmunks also feed heavily on acorns and they, along with squirrels, harbor Lyme. This year there are lots of small woodland mammals the ticks can attach themselves too. Next year, not so much. With far fewer wild mammals the ticks will be looking to people and furry pets for their next meal.
 Well hello there little mouse! My husband Tom was releasing a mouse that was caught in his have-a-heart trap. He first opened opened the front door of the trap, with no sign of movement within, and then the back door. After a few minutes passed, out ran the little mouse, but then he froze in his tracks, only several feet from where I was standing. As I was motionless taking his photo, I think he must have thought I was a tree. He suddenly ran up my leg, up under my dress, and poked his head out from beneath my coat. It’s too bad I was holding the camera and not my husband!
Well hello there little mouse! My husband Tom was releasing a mouse that was caught in his have-a-heart trap. He first opened opened the front door of the trap, with no sign of movement within, and then the back door. After a few minutes passed, out ran the little mouse, but then he froze in his tracks, only several feet from where I was standing. As I was motionless taking his photo, I think he must have thought I was a tree. He suddenly ran up my leg, up under my dress, and poked his head out from beneath my coat. It’s too bad I was holding the camera and not my husband!
Thinking about hantavirus, and just to be on the safe side, I changed my clothes and washed immediately.
Studies show how the increasing Eastern Coyote population has impacted White-footed Mice, Red Fox, and the explosion of Lyme disease. In areas where the Eastern Coyote has outcompeted the Red Fox for habitat, Lyme disease has increased. Coyotes not only kill Red Fox, they simply aren’t as interested in eating mice as are the fox.
Answer: Both the White-footed and Deer Mouse carry hantavirus, not the House Mouse. To be on the safe side, if you find rodent droppings in your home or office, do not vacuum because that will disperse the virus throughout the air. Instead, wipe up with a dampened paper towel and discard.
Read more about the White-footed Mouse and Lyme disease here: The Mighty White-footed Mouse
Reminder- Dogtown could be eligible for the National Register. A team of archaeologists began surveying and reviewing Dogtown the week of November 13. Come to a special public presentation TONIGHT – November 29th in Kyrouz Auditorium, Gloucester City Hall, 9 Dale Avenue, at 7pm.

Oct 28 GMG post announcing tonight’s public meeting: Before Dogtown was Dogtown: archaeological survey project to be presented at City Hall November 29! Maybe hello blueberries bye bye lyme disease
“Presenters at City Hall on Nov 29th will include Betsy Friedberg from the Massachusetts Historical Commission, who will explain how the National Register program works and what it does and does not do, and Kristen Heitert from the PAL, who will present an initial plan for defining the boundaries of Dogtown as a National Register District. People attending the meeting will be asked to respond to that plan and to express their views about what makes Dogtown special. What should be the boundaries of the proposed National Register District, and what cultural features should be included in it? What would be the benefits of National Register status, and are there any drawbacks?”



Sharing press release from Mary Ellen Lepionka and Bill Remsen followed by a selection of visual arts, maps, and writing spotlighting Dogtown (1633-1961) by Catherine Ryan.
Nov 29th, 7PM, Public Meeting
Come to a special public presentation November 29th in Kyrouz Auditorium in Gloucester City Hall, 9 Dale Avenue, at 7pm.
Week of Nov 13
“During the week of November 13 a team of archaeologists from the Public Archaeology Laboratory (PAL) in Providence will be conducting fieldwork in Dogtown. They will begin mapping and describing an area to be nominated to the National Register of Historic Places, a National Park Service program to honor historically significant buildings and landscapes.
What do you think?
“Presenters at City Hall on Nov 29th will include Betsy Friedberg from the Massachusetts Historical Commission, who will explain how the National Register program works and what it does and does not do, and Kristen Heitert from the PAL, who will present an initial plan for defining the boundaries of Dogtown as a National Register District. People attending the meeting will be asked to respond to that plan and to express their views about what makes Dogtown special. What should be the boundaries of the proposed National Register District, and what cultural features should be included in it? What would be the benefits of National Register status, and are there any drawbacks?
Who all is involved?
“The Dogtown archaeological survey is funded through a matching grant from the Massachusetts Historical Commission and the Dusky Foundation and is financed by the City of Gloucester. The Gloucester Historical Commission applied for the grant and is coordinating the project in collaboration with the Rockport Historical Commission. The PAL team will also have the assistance of members of the Dogtown Advisory Committee, the Rockport Rights of Way Committee, the Cape Ann Trail Stewards, and the Friends of Dogtown.”
– Dogtown is eligible for the National Register. Will Gloucester earn another major district designation? Above excerpts from the press release for the Nov 29th event shared by Bill Remsen, local project coordinator, and Mary Ellen Lepionka, co-chair Gloucester Historical Commission, and some Dogtown maps and memorabilia 1633-1961
Prior 2017 Dogtown public forums, lectures and meetings mentioned consideration of controlled burns to clear brush and return some land to a former moors state, with various potential benefits.
from books, and memorabilia I’ve pulled on Dogtown (1634-1961):
From Gloucester 1961 Cape Ann Festival of the Arts booklet
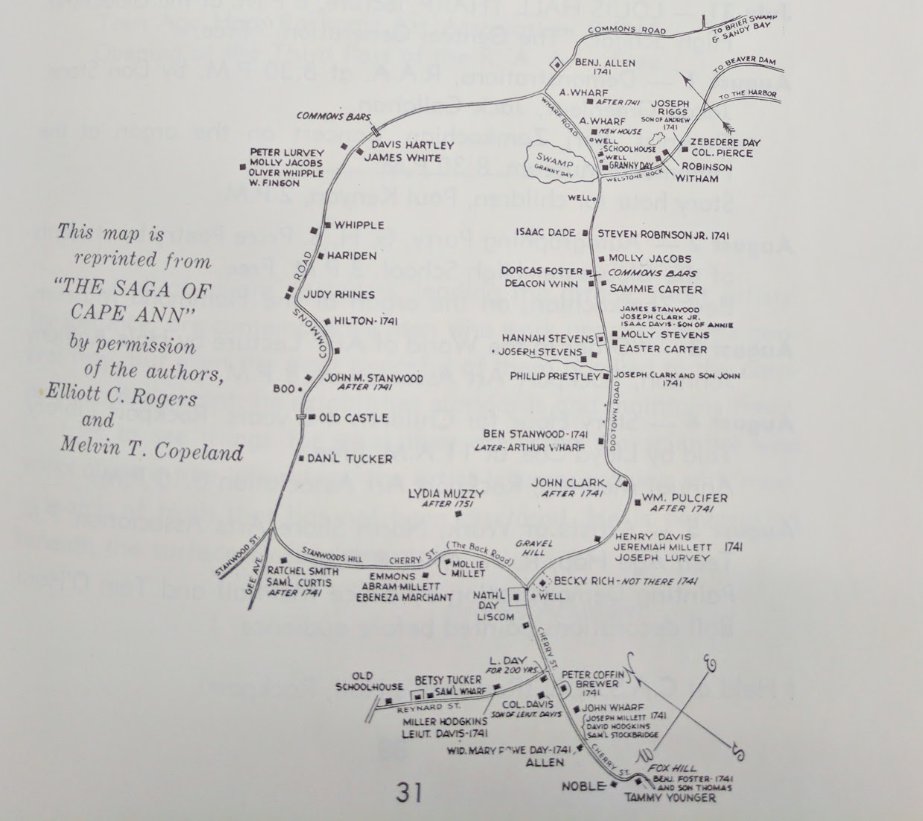
From Gloucester 1954 Festival of the Arts booklet, prepared for the second of the Russel Crouse Prize Play, the Witch of Dogtown, by S. Foster Damon. “Each year it is hoped new plays dealing with the Gloucester or Cape Ann theme will be produced.”

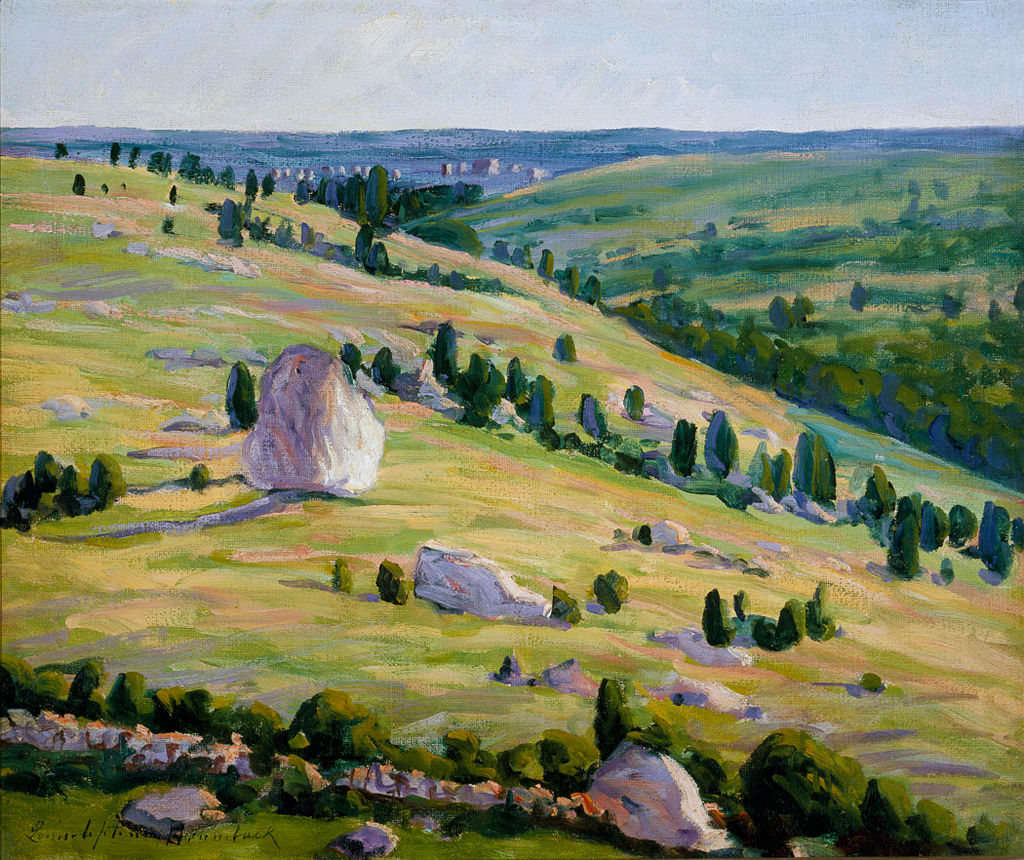
“Dogtown Common, the now deserted hill home of the first settlers who 300 years ago braved the dangers of a hostile and Indian Annisquam, offers both romance and reality. It has remained for Louise Upton Brumback to interpret its clear contrasts, its far spaces, blue skies, white clouds and stiff green pointed cedars. Although the draftsmanship is crude in the extreme, the effect is rare and genuine. The old resident who passes through the gallery will shake his head dubiously at the false color creations of harbor and rock, but accepts this striking and bold visualization of Dogtown Common as the true spirit of Cape Ann…”

Inland among the lonely cedar dells
Of Old Cape Ann, near Gloucester by the Sea,
Still live the Dead–in homes that used to be.
All day in dreamy spells
They tattle low with sounds of tinkling cattle
bells
Or spirit tappings of some hollow tree
And there, all night–out of the
dark–
They bark–and bark…
“Note: From a little volume, by Charles E. Mann, entitled “In the Heart of Cape Ann” Gloucester, Mass., The Proctor Bros. Co), the curious reader may learn more strange, half forgotten facts concerning the old Puritan life of that region. Among its singular New England characters, certain authentic and legendary figures have entered the theme of this poem.
P.M-K. Miami University, Oxford, Ohio. March, 1921
Percy MacKaye (1875–1956) was an American dramatist and poet.
Harvard MacKaye papers: “History note: Percy Wallace MacKaye, author and dramatist, graduated from Harvard in 1897, wrote poetic dramas, operatic libretti, modern masques and spectacles, and was active in promoting community theatre. The collection includes his papers and those of his wife, Marion Homer Morse MacKaye, as well as material relating to the career of his father Steele MacKaye (1842-1894), an American theatrical designer, actor, dramatist, and inventor. The bulk of the collection consists of material pertaining to community drama; correspondence with literary and theatrical figures including Edgar Lee Masters, Edwin Arlington Robinson, George Pierce Baker, Theodore Dreiser, Amy Lowell, Upton Sinclair, Edward Gordon Craig, Louis Untermeyer and Thornton Wilder.”
Dartmouth: The MacKaye Family Papers “contain materials documenting the life and career of four generations of the family. They include a large amount of personal and professional correspondence as well as original manuscripts and typescripts of plays, prose, masques, pageants, poetry, essays and articles. Of note are manuscript materials for Benton MacKaye’s works on geotechnics entitled “Geotechnics of North America,” and “From Geography to Geotechnics,” as well as Percy MacKaye’s biography and works on his father Steele MacKaye and the MacKaye family, entitled respectively, “Epoch,” and “Annals of an Era.”
(Gloucester, Dogtown Common, is not on the MacKaye Wikipedia page)
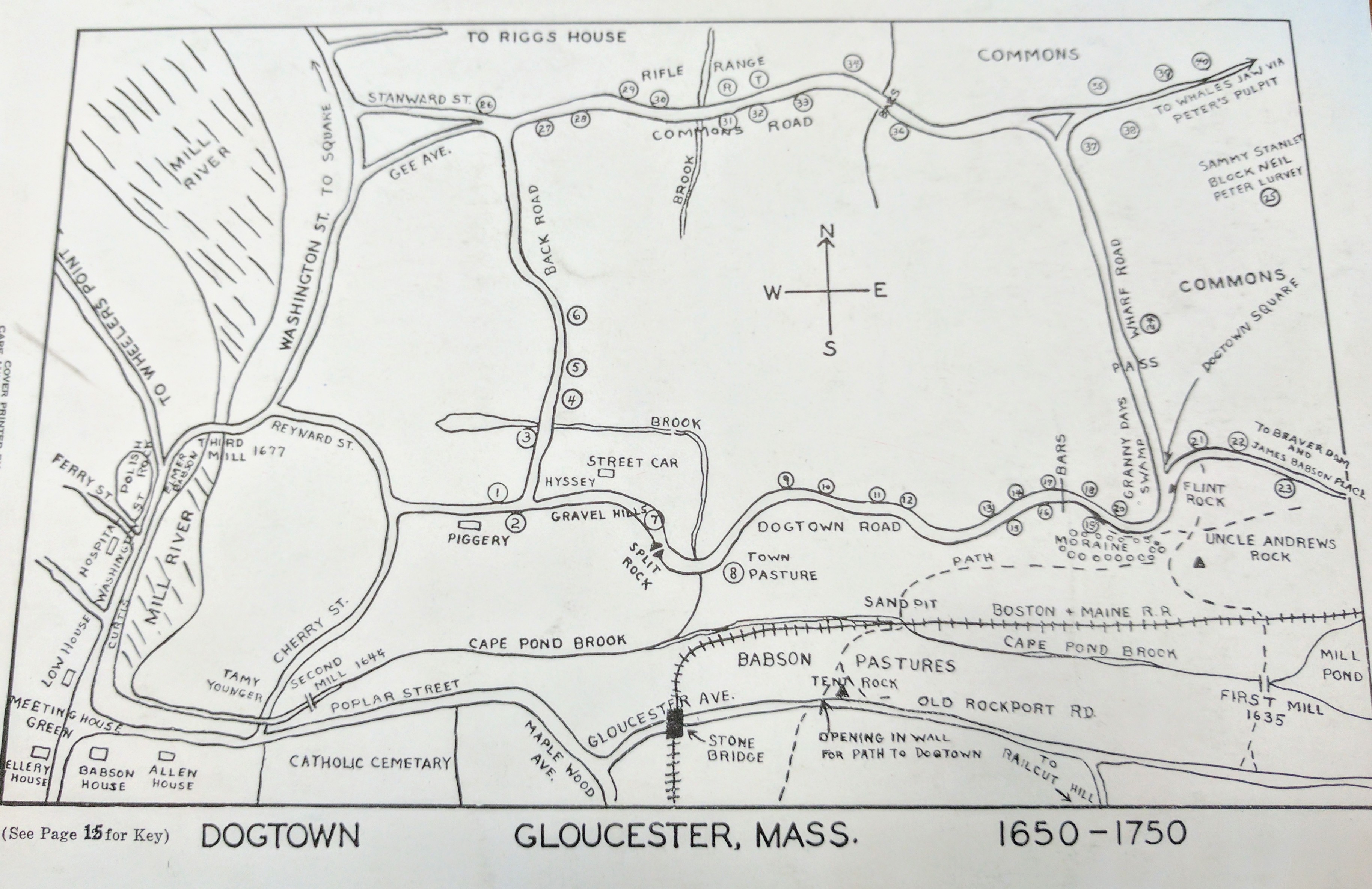
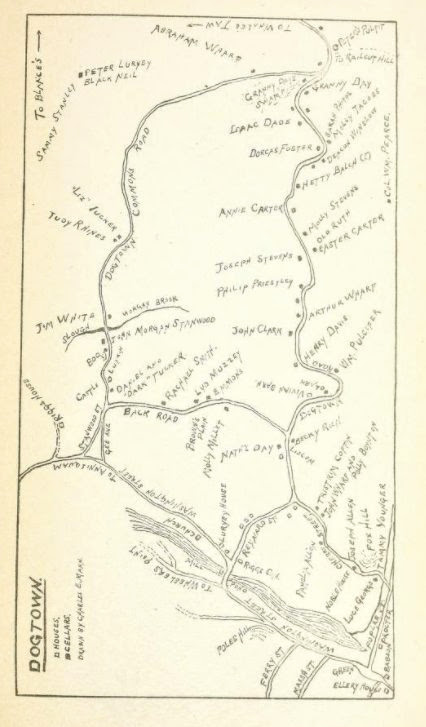
Business owner, photographer, author Frank L Cox devoted 7 pages and 4 photographs to illustrate the Dogtown and Its Story chapter


“Just to the left of the road at the top of Gee Avenue is one of the most celebrated ceallar in Dogtown. It is that of John Morgan Stanwood, who was mistakenly made famous by a poem by Hiram Rich, published in the Atlantic…”




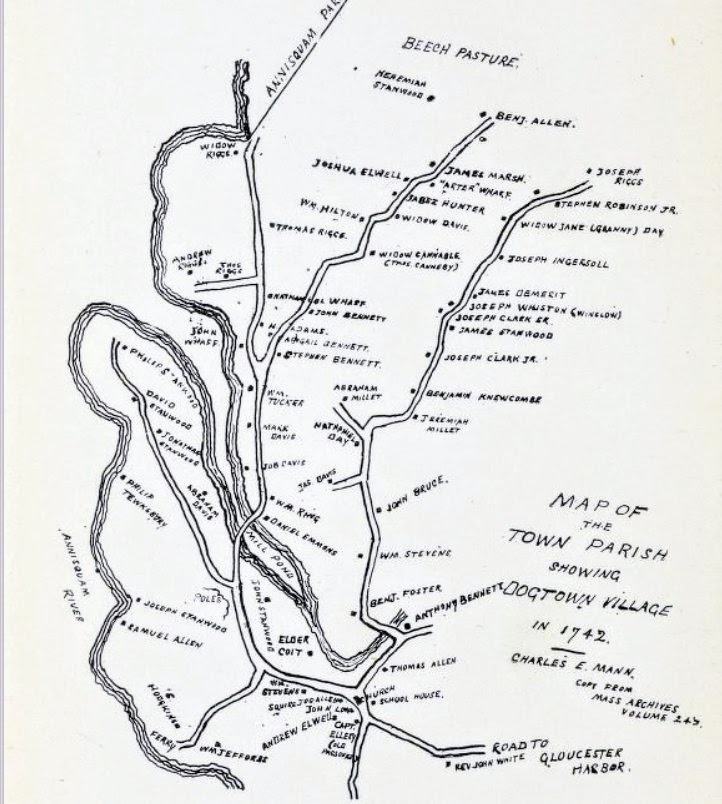
“Three miles inland, as I remember, we found the hearthstones of a vanished settlement; then we passed a swamp with cardinal flowers; then a cathedral of noble pines, topped with crow’s-nests. If we had not gone astray by this time, we presently emerged on Dogtown Common, an elevated table-land, over spread with great boulders as with houses, and encircled with a girdle of green woods and an outer girdle of blue sea. I know of nothing more wild than that gray waste of boulders..”
Dogtown, Cape Ann, described in Footpaths chapter Oldport Days
on clearing land…
In 1855, Henry David Thoreau wrote in his journal: “I am [reading] William Wood’s “New England’s Prospect”… William Wood New Englands Prospect was originally published in 1634 in London. Here is a Wood excerpt concerning burning brush to clear land, a historical antecedent (and apt surname) to keep in mind when considering stewardship 2017 and beyond.
…The next commodity the land affords is good store of woods, and that not only such as may be needful for fuel but likewise for the building of ships and houses and mills and all manner of water-work about which wood is needful. The timber of the country grows straight and tall, some trees being twenty, some thirty foot high, before they spread forth their branches; generally the trees be not very thick, though there may be many that will serve for mill posts, some being three foot and a half over. And whereas it is generally conceived that the woods grow so thick that there is no more clear ground than is hewed out by labor of man, it is nothing so, in many places diverse acres being clear so that one may ride a hunting in most places of the land if he will venture himself for being lost. There is no underwood saving in swamps and low grounds that are wet, in which the English get Osiers and Hasles and such small wood as is for their use. Of these swamps, some be ten, some twenty, some thirty miles long, being preserved by the wetness of the soil wherein they grow; for it being the custom of the Indians to burn the wood in November when the grass is withered and leaves dried, it consumes all the underwood and rubbish which otherwise would overgrow the country, making it unpassable, and spoil their much affected hunting; so that by this means in those places where the Indians inhabit there is scarce a bush or bramble or any cumbersome underwood to be seen in the more champion ground. Small wood, growing in these places where the fire could not come, is preserved. In some places, where the Indians died of the plague some fourteen years ago, is much underwood, as in the midway betwixt Wessaguscus and Plimouth, because it hath not been burned. Certain rivers stopping the fire from coming to clear that place of the country hath made it unuseful and troublesome to travel thorow, in so much that it is called ragged plaine, because it teares and rents the cloathes of them that pass. Now because it may be necessary for mechanical Artificers to know what timber and wood of use is in the Country, I will recite the most useful as followeth*…” *see photos for Wood’s trees list
Thoreau was thinking along these lines, finding god in berries.
“From William Wood’s New England’s Prospect, printed about 1633, it would appear that strawberries were much more abundant and large here before they were impoverished or cornered up by cultivation. “Some,” as he says, “being two inches about, one may gather half a bushel in a forenoon.” They are the first blush of a country, its morning red, a sort of ambrosial food which grows only on Olympian soil.” -Thoreau’s Wild Fruit
“If you look closely you will find blueberry and huckleberry bushes under your feet, though they may be feeble and barren, throughout all our woods, the most persevering Native Americans, ready to shoot up into place and power at the next election among the plants, ready to reclothe the hills when man has laid them bare and feed all kinds of pensioners.”
photos: William Wood’s New Englands Prospect scanned from book in the University of CA collection. “Wonasquam” on map at Cape Ann




“Of their Custom in burning the Country, and the reason thereof”
The Salvages are accustomed to set fire of the Country in all places where they come, and to burne it twice a year: at the Spring, and the fall of the leaf. The reason that moves them to do so, is because it would other wise be so overgrown with underweeds that it would be all a coppice wood, and the people would not be able in any wise to pass through the Country out of a beaten path…
And this custom of firing the Country is the meanes to make it passable; and by that meanes the trees growe here and there as in our parks: and makes the Country very beautiful and commodious.”

Jim Dowd shares the following very excellent article about Lyme with important guidelines.
On a visit to Martha’s Vineyard Hospital, Dr. Nevena Zubcevik challenged conventional diagnosis and treatment of tick-borne diseases.
This past Friday, Dr. Nevena Zubcevik, attending physician at Harvard Medical School and co-director of Dean Center for Tick Borne Illness at Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital in Charlestown (SRH) traveled to one of the nation’s front lines in the public health battle against Lyme disease to speak to a group of Martha’s Vineyard Hospital physicians. “I wanted to do this presentation by Skype because of all the ticks you have here,” she joked.
Dr. Zubcevik was at Martha’s Vineyard Hospital (MVH) to speak at grand rounds, a weekly meeting of clinicians, which on this day was open to the public, resulting in an overflow crowd at the Community Room just off the hospital lobby.
Over the course of the hour, she shared the most recent findings that she and her colleagues have made on the diagnosis and treatment of Lyme disease, in particular on the 10 to 15 percent of patients who suffer long-term symptoms, defined by Centers for Disease Control (CDC) as post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome (PTLDS). She discussed the protean nature of tick-borne diseases, the importance of public awareness, and the urgent need for the medical community to step up its game.
“Graduating medical students and doctors really aren’t educated about the gravity of this epidemic,” she said. “There’s a gap there that needs to be filled. We’re all responsible to educate our young doctors about what this entails.”
Dr. Zubcevic said the recent revelation that actor, singer, and songwriter Kris Kristofferson was cured of dementia once he was properly diagnosed with Lyme disease should be a lesson for medical professionals on how pervasive the disease is, and how often it is overlooked.
“Sudden-onset dementia should really be a red flag for Lyme [disease], especially in people with compromised immune systems,” she said.
“Everyone over 50 has a compromised immune system.”
Did you know that ticks carry a number of diseases beside Lyme disease? Two that in recent years have reared their ugly heads on Cape Ann are anaplasmosis and babesiosis. Both are transmitted by the black-legged tick (deer tick) in the northeastern U.S. and both have similar symptoms. When symptoms are exhibited, blood is drawn to determine which pathogen is present.
Recently I was bitten by a black-legged tick. The tick was only on my person for several hours. I brushed it off before realizing that it was a tick. The tick was completely flat and not in the least bit engorged. It left a slightly red raised bump that was itchy for a week or so. At my doctor’s office the staff insisted that because the tick was not engorged and because it was attached for less than twenty four hours I was safe from disease. This information was also reinforced by reading about Lyme disease on countless websites.
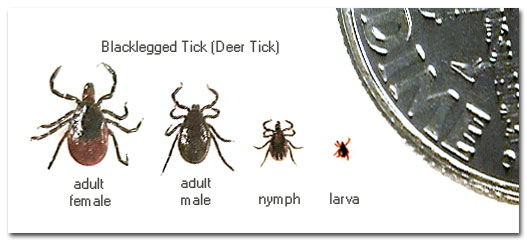 Ticks of all sizes and at all stages of life can harbor diseases
Ticks of all sizes and at all stages of life can harbor diseases
That you cannot get sick from a tick attached for less than twenty four hours is 100 percent false. Several weeks ago I staggered home from a very busy day planting a client’s garden. I thought perhaps I had just overdone it and went straight to bed. The next day I could barely move. For the next two weeks I would make an effort to get to work but wind up back in bed a few short hours later. I at first thought it was the flu, but instead of running its course and getting better, things went from bad to worse until I ended up in the hospital with pneumonia. That’s one of the things with anaplasmosis, it also effects your respiratory system.
Kelly Ries, Gloucester’s public health nurse shares that less than five cases of anaplasmosis and babesiosis have been reported in Gloucester. Symptoms of anaplasmosis include fever, headache, muscle pain, malaise, chills, nausea, abdominal pain, cough, confusion, and loss of appetite, of which I had all.
I am writing to help create an awareness with our readers that Lyme disease is not the only pathogen carried by the black-legged tick. Each year, more and more cases of anaplasmosis and babesiosis are being diagnosed in the northeast. Nurse Kelly also reports that black-legged ticks are still active at this time of year and can continue to transmit disease even after the first snowfall of the season. If any of our readers have contracted anaplasmosis (which I sincerely hope not) please write and let us know your experience. Thank you so much.
Doxycycline is the first line of defense for adults and children of all ages and should be initiated immediately whenever anaplasmosis is suspected however, the CDC website provides a warning regarding prophylaxis (preventative treatment): Antibiotic treatment following a tick bite is not recommended as a means to prevent anaplasmosis. There is no evidence this practice is effective, and this may simply delay onset of disease. Instead, persons who experience a tick bite should be alert for symptoms suggestive of tickborne illness and consult a physician if fever, rash, or other symptoms of concern develop.
For more information about about anaplasmosis see the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention here.
As you can see from the map below, prior to 2010, there were zero cases of anaplasmosis reported in Massachusetts.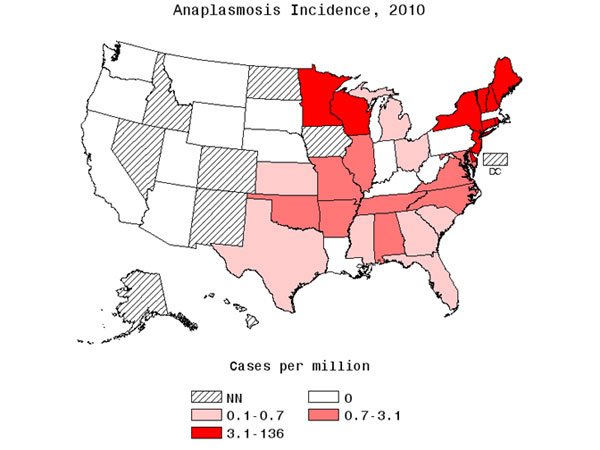

Are Coyotes the Cause of an Increase in Lyme Disease?
Struck by the recent interest in coyotes after the fascinating video Two Coyotes Versus One Deer by Shawn Henry was posted on GMG, I became interested in reading various studies and reports about coyotes, wolves, and foxes in Massachusetts and the Northeast. My primary interest at the onset was of concern for the Red Fox (Vulpes vulpes), which has seen a tremendous decline in numbers. I wondered if the presence of coyotes (Canis latrans) was negatively impacting the Red Fox. In the past, I often saw a Red Fox in the early morning hours trotting along the shoreline at Brace Cove. I wish so much that I had filmed the last one that I saw because it was a gorgeous scene; a strikingly beautiful creature so completely unaware of my presence and so at home in its realm, investigating rock and seaweed, pausing to sniff the air, and then resuming its journey. The last time I saw a Red Fox in our neighborhood was over three years ago. As I was reading about coyotes I learned the findings of some of the most recent studies indicate that because Eastern Coyotes out-compete the Red Fox, the coyotes are the cause of an increase in Lyme disease. More on that in a moment.
The coyotes that now inhabit every region in Massachusetts are an invasive species. They are a hybrid cross species of the Western Coyote (found west of the Mississippi) and Red Wolf (Canis lupus rufus). “Researchers now believe that the Eastern Coyote is a hybridization between the Western Coyote and Red Wolf many generations ago in the upper Great Lakes region of the United States. It is theorized that as populations of the Western Coyote increased, they were forced to move east and north in search of food. As they moved into Minnesota they crossbred with Gray/Red Wolves and produced a genetically hardy animal able to sustain itself through New England winters.” (Mass Audubon)
Coyotes are not “re-populating” this region because this new species was never in our region.
Eastern Coyotes have extremely broad food habits and many factors affect the coyotes’ diet, including competition with other mammals, abundance of prey, season, and weather. In the Northeast, their diet consists of shrews, rabbits, voles, woodchucks, mice, deer, beaver, muskrat, weasels, squirrels, and carrion. And according to Mass Audubon, “They eat ground-nesting birds and their eggs, as well as reptiles and amphibians. When other prey is scarce they will eat a variety of insects including grasshoppers, beetles and cicadas. When animal matter is scarce, they will eat available fruits including apples, cherries, grapes, and strawberries.”
The rapid invasion of the alien Eastern Coyote has negatively impacted many sympatric native species, as the coyote has assumed the role of top-order predator. The coyote has fundamentally altered the existing ecosystem and various species have experienced population declines as a direct result of their role as coyote prey or from direct competition for food. “Culturally and ecologically significant species including Red Fox decline dramatically in response to increasing coyote populations. Eastern Coyote and Red Fox share many common habitat requirements and occupy overlapping niches. Through time, the larger and more resilient coyote is able to out-compete and displace resident fox populations.” (Department of Natural Resources, Maryland.)
Studies have shown repeatedly that Eastern Coyote predation on deer is minimal. Most herds can handle the coyotes. Typically coyotes have success with fawns that are 4-5 weeks old (after they have become more active and are not by the mother’s side), weakened and sickly adults, and deer separated from the herd. These targets represent approximately one or two percent of the total deer population. While coyote diet studies show consistently the use of deer for food, it does not appear that coyote limit deer population on a regional scale.
Although the population of White-tailed Deer has stabilized, Lyme disease continues to increase. In June of 2012 researchers at the University of California Santa Cruz published their findings from the study “Deer, Predators, and the Emergence of Lyme Disease.” (Taal Levi, lead author.)
The study found that once where there was an abundance of Red Foxes, there is now an abundance of Eastern Coyotes. Even more significantly, fewer coyotes will inhabit an area once populated by more foxes. The greater number of foxes would have consumed a larger number of small tick-bearing animals, primarily White-footed Mice, Short-tailed Shrews, and Eastern Chipmunks, all of which transmit Lyme disease bacteria to ticks. It appears as though it is the Red Fox that once kept the population of these smaller rodents under control.
Even when there is a threefold rise in deer population, study after study now shows that the strongest predictors of a current year’s risk of Lyme disease are an abundance of acorns two years previously. How does that work?
Many acorns = many healthy mice and chipmunks.
Many healthy mice and chipmunks = many tick nymphs.
The following year when it may not be a bumper acorn crop = fewer mice.
Fewer mice and chipmunk = dogs and humans become vectors for the ticks.
While acorns don’t serve as a universal predictor because Lyme disease can be traced to forests where there are no oak trees, the data suggest that food sources and predators of small forest mammals are likely to be valuable in predicting Lyme disease risk for humans.
To summarize, multiple studies suggest that the invasive Eastern Coyote out-competes and kills the native Red Fox population, which leads to a rise in the number of small animals particularly the White-footed Mouse and Eastern Chipmunk, which in turn leads to an increase in ticks that carry Lyme disease. The impact of the Eastern Coyote on native deer population is negligible. And, as many family’s can attest, the impact of the Eastern Coyote on populations of domestic cats and small dogs has been devastating.
Typically the excuse given for unwanted encounters with wildlife is that people are encroaching on the animal’s habitat. That simply is not the case with the Eastern Coyote. The Eastern Coyote is advancing on humans–and they like what they see; no large predators, a reluctance on the part of people to hunt and trap, and an abundance of food. The environmentally and culturally destructive chain reaction caused by the Eastern Coyote invasion is taking on added urgency as the coyote strikes closer and closer to home.
It is legal in the state of Massachusetts to shoot and kill a coyote from your home. If confronted by a coyote, make as much noise as possible, if attacked, fight back aggressively.
Images courtesy Google image search.
Everyone knows that coyotes have moved onto Cape Ann and Cape Cod but did you know they are actually a new hybrid with the eastern wolf? The DNA typing of this new species is just in its infancy. Mostly using mitochondrial DNA to get a rough understanding but now that genomic sequencing is much cheaper a more detailed picture is forming. Some coyotes trapped have come up as 90% eastern wolf DNA! These hybrids, I’ll call them coywolf from now on, are bigger than coyotes. They are very sociable, live in family packs and can have a range of ten square miles. That is a decent chunk of Cape Ann. I would guess though if the food is plentiful they would hang in one region near their den.
Should you be fearful of these coywolves? You shouldn’t. In fact we should be happy they are here. They fill the niche that the wolf filled here for centuries and now she is back. They eat deer, mice, rabbits, all those small animals. The deer and mice are key. Lyme disease has a life cycle that explodes when deer and mice populations increase. Knocking down both of these populations will keep Lyme disease in check.

Yes, the coywolves will eat your cat but your cat should not be out there anyway. Feral and outdoor cats eat more than 3 billion birds in the US annually. You can’t blame them. They have been trained to do this since ancient egyptian times protecting granaries from vermin. They don’t even eat them just killing one bird after another. Keep your cat inside and let these coywolves keep the population of Lyme disease plagued vermin like deer and mice down to tolerable levels. They are a perfect fit for Cape Ann. They don’t like to eat birds. And if you find a dead coywolf I need just a very small blood sample to run a genetic haplotype test to see how much of a wolf she was. But please do not hunt them. They are doing us all a big favor. Imagine going for a hike in Dogtown and having no fear of being covered by disease ridden deer ticks. If you’ve had Lyme disease you should kiss a wolf on the lips for moving into your neighborhood. They might even take out a fishercat or two.
If the genetic testing of the coywolves on Cape Ann come up as over 80% wolf DNA we can drop the hybrid coywolf name. That is a wolf.
[3/26/13 edit] Lots of great comments on this article. For some local information on wolves go to Wolf Hollow in Ipswich: