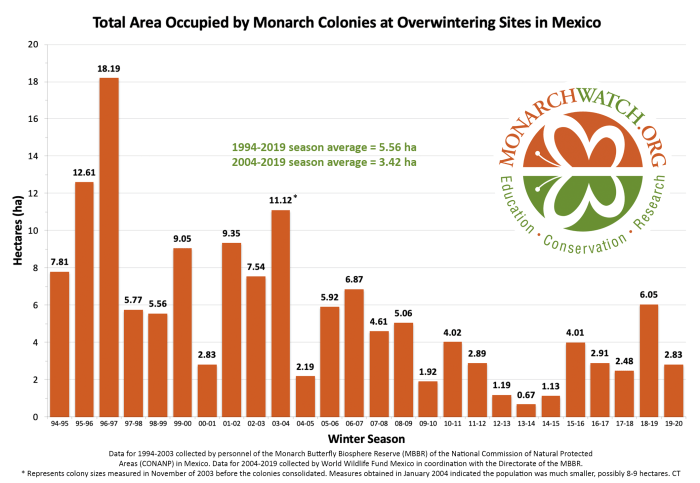
How disappointing to see the Monarch numbers plunge to less than half of last year’s population. Scientist Chip Taylor from Monarch Watch predicted lower numbers, but not to this degree. It’s hard to believe, especially after witnessing the tremendous numbers at Cerro Pelon in 2019, along with the beautiful migration through Cape Ann last summer.
How disappointing to see the Monarch numbers plunge to less than half of last year’s population. Scientist Chip Taylor from Monarch Watch predicted lower numbers, but not to this degree. It’s hard to believe, especially after witnessing the tremendous numbers at Cerro Pelon in 2019, along with the beautiful migration through Cape Ann last summer.
 Plant a variety of milkweeds and wildflowers to help the Monarchs on the northward and southward migrations
Plant a variety of milkweeds and wildflowers to help the Monarchs on the northward and southward migrations
The chief reasons for this year’s loss of Monarchs are decreasing amounts of wildflowers on their migratory route south, bad weather during the 2019 migration, and the continued spraying of deadly chemical herbicides and pesticides on genetically modified food crops.
As we are all aware, Monarch caterpillars only eat members of the milkweed (Asclepias) family, but the plant has been devastated by increased herbicide spraying in conjunction with corn and soybean crops that have been genetically engineered to tolerate direct spraying with herbicides. In addition to glyphosate (Monsanto’s Roundup, which is now owned by Bayer), Monarchs are threatened by other herbicides such as Dicamba and by neonicotinoid insecticides that are deadly poisonous to young caterpillars and decrease the health of adult butterflies.
In 2014, conservationists led by the Center for Biological Diversity and the Center for Food Safety petitioned the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service to protect the butterfly under the Endangered Species Act.
The decision on Endangered Species Act protection will be issued in December of this year under a settlement with the conservation groups. The low count of 2019-2020 reinforces the need to protect what we already know to be an endangered species.